
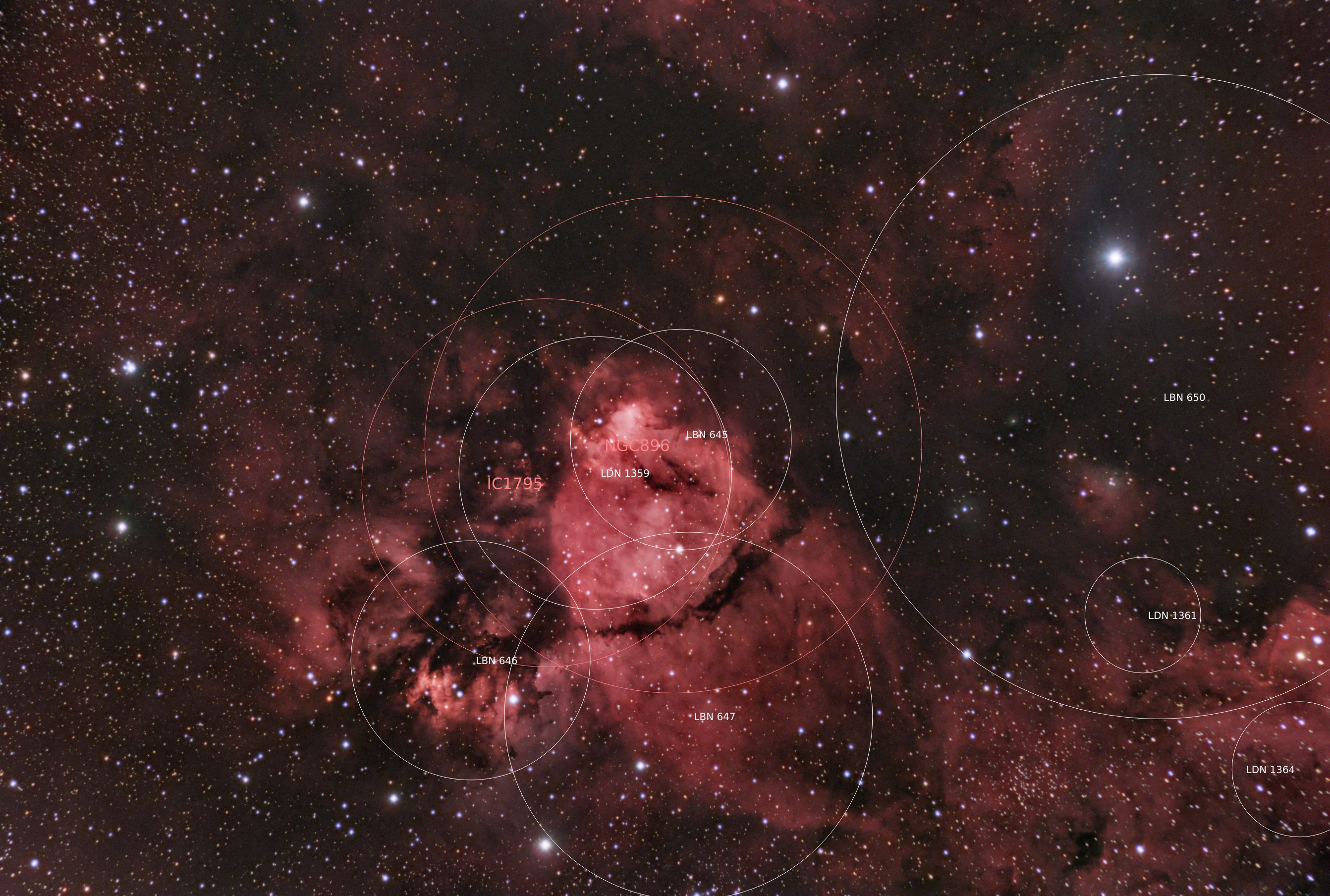
- Constellation: Cassiopeia
- Right Ascension: 02h 33m 22s
- Declination: +61° 26′ 36″
- Distance: 7,500 ly
NGC 896 is an H II emission nebula located in Cassiopeia. More commonly know as the Heart Nebula.

- Details
- Category: Nebulas
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

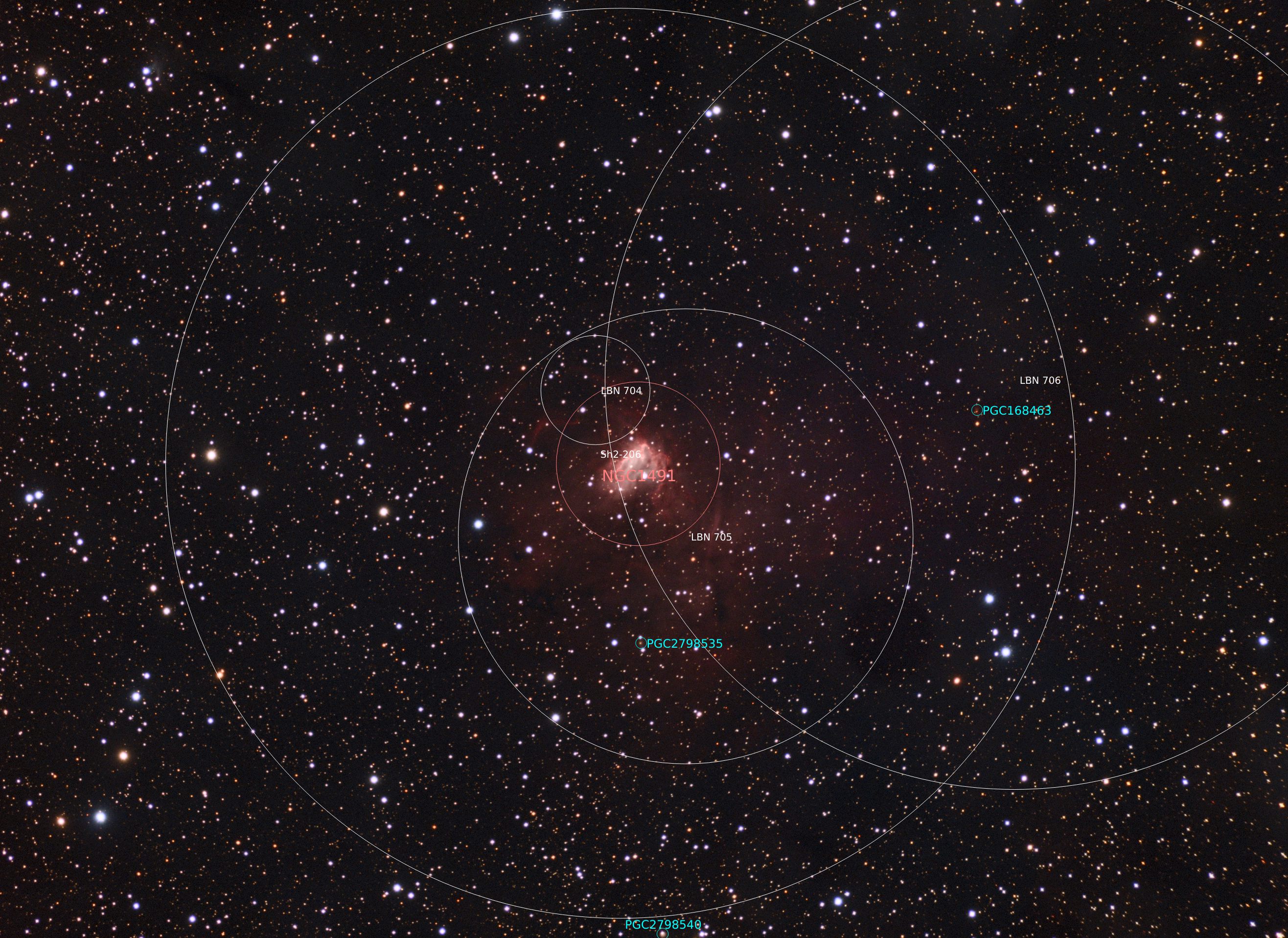
- Constellation: Perseus
- Right Ascension: 04h 03m 15.9s
- Declination: +51° 18′ 54″
- Distance: 9,800 ly approximate
NGC 1491 is a emission nebula located in the constellation of Perseus. It is often referred to as the Fossil Footprint nebula. Massive stars located in the nebula ionize the hydrogen gas causing it to glow in red light.

- Details
- Category: Nebulas
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

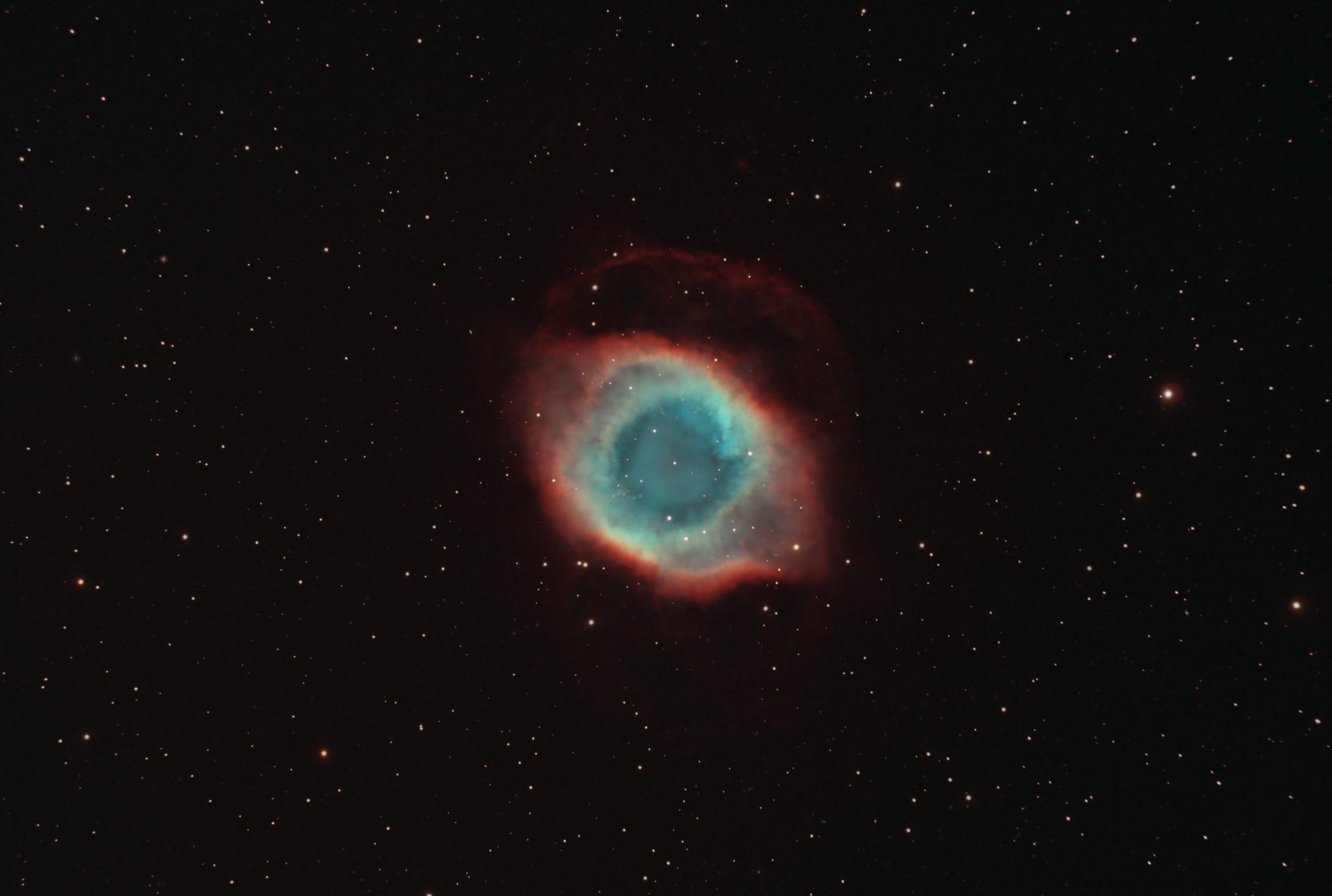
- Constellation: Aquarius
- Right Ascension: 22h 29m 38.55s
- Declination: −20° 50′ 13.6″
- Distance: 650 ly
NGC 7293 aka Helix nebula is one of the closest of the planetary nebula which is formed from a lower mass star that sheds it's outer layers near the end of it's life before shrinking down to a white dwarf.
Following image taken using narrow band filters, Ha, OIII, and SII.
- Details
- Category: Nebulas
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

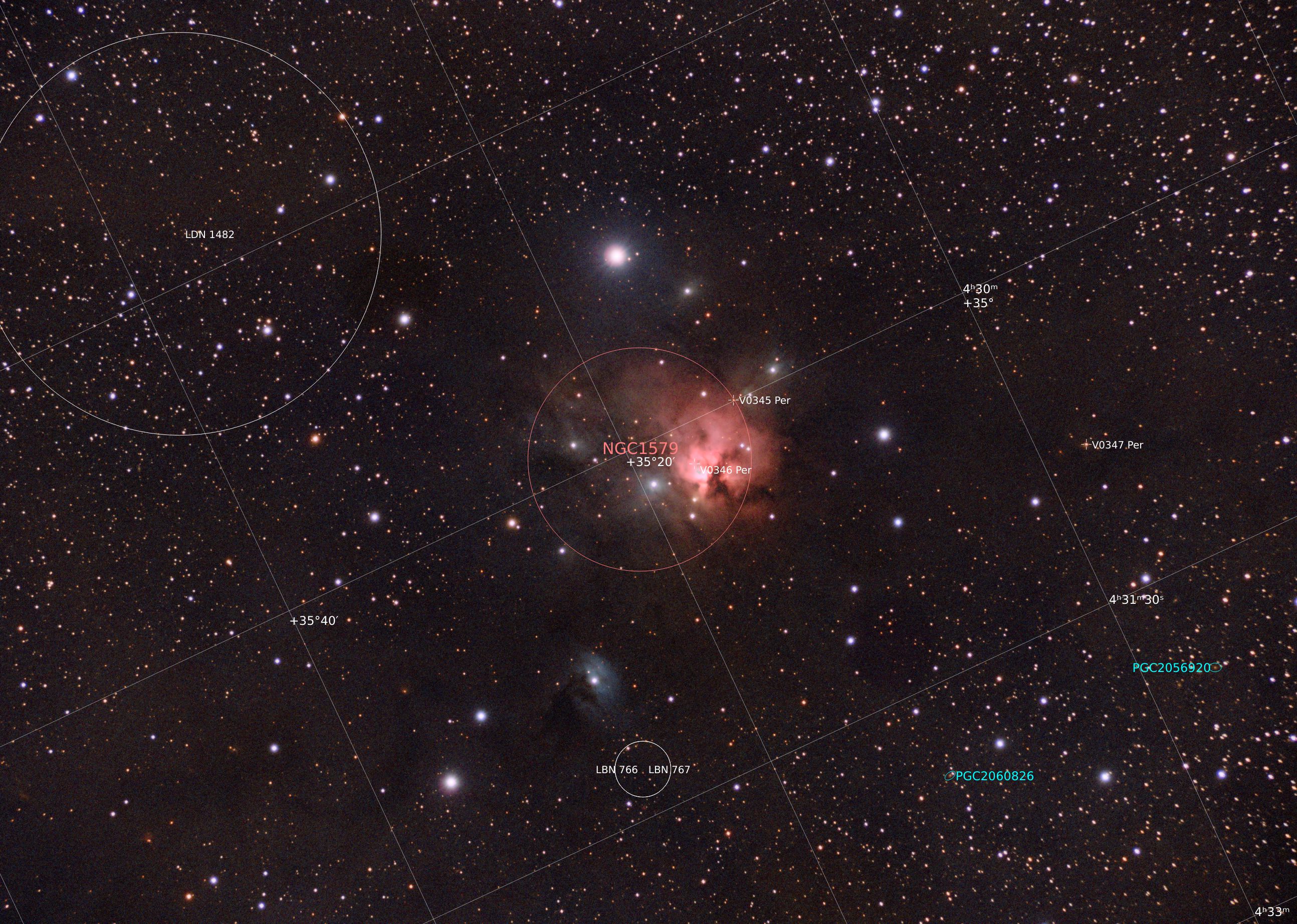
- Constellation: Perseus
- Right Ascension: 04h 30m 09.5s
- Declination: +35° 16′ 19″
- Distance: 2,100 ly
NGC 1579 is a nebula located in the constellation of Perseus. Often called the Northern Trifid because of its similarity to the Trifid nebula.

- Details
- Category: Nebulas
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

- Constellation: Aquarius
- Right Ascension: 21h 04m 10.877s
- Declination: −11° 21′ 48.25″
- Distance: 2,000 - 4,000 ly
NGC 7009 is a planetary nebula located in Aquarius. Of course the name comes from its resemblance to the planet Saturn. The way a planetary nebula forms of course is way different. A low mass star loses its outer layers during it's red giant phase before shrinking down in to a white dwarf. The nebula is glows from the ionization from the now white dwarf.
- Details
- Category: Nebulas
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

- Constellation: Cygnus
- Right Ascension: 20h 01m 48.1s
- Declination: +33° 31' 33"
- Distance: 28,000 ly
NGC 6857 was originally categorized as a planetary nebula, but its actually just a denser part of a larger HII region called Sharpless 2-100.
- Details
- Category: Nebulas
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM