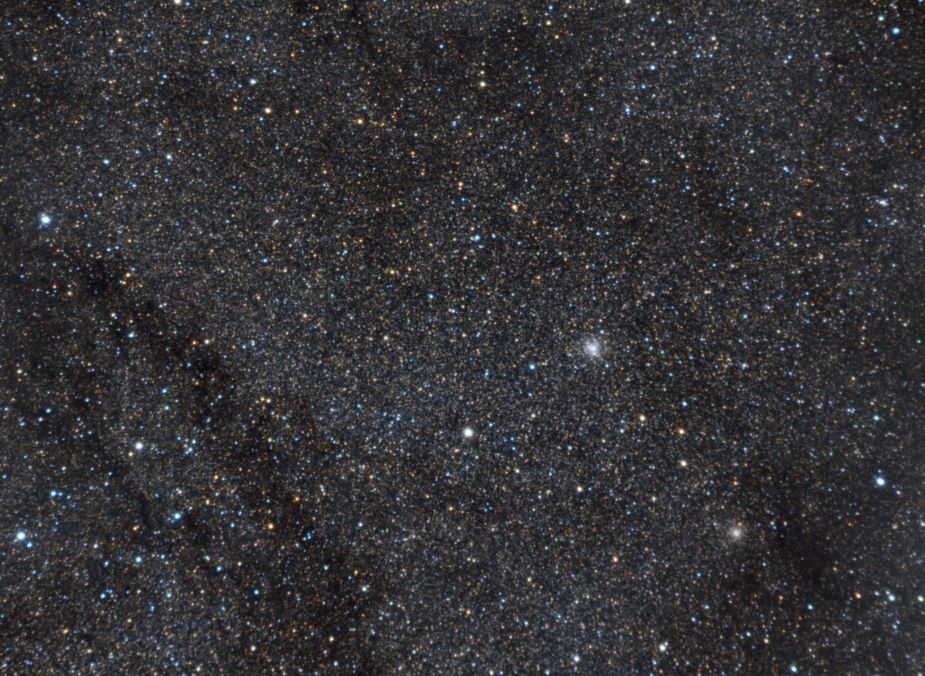
NGC 6791 (2024)
- Constellation: Lyra
- Right Ascension: 19h 20m 53s
- Declination: +37° 46.3′
- Distance: 13,300 ly
NGC 6791 is an open star cluster located in the constellation of Lyra. One of the oldest known clusters, its age is estimated to be 8 billion years. A heavily studied cluster and was also in the field of view of the Kepler space telescope that was designed to look for planet transits.
- Details
- Category: Open Clusters
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

NGC 6755 and NGC 6756 (2024)
- Constellation: Aquila
- Right Ascension: 19h 07m 46.1s
- Declination: +04° 13′ 26″
- Distance: 8,060 ly
NGC 6755 is an open cluster located in the constellation of Aquila. Its estimated age is 250 million years. It has a Trumpler classification of II2r.
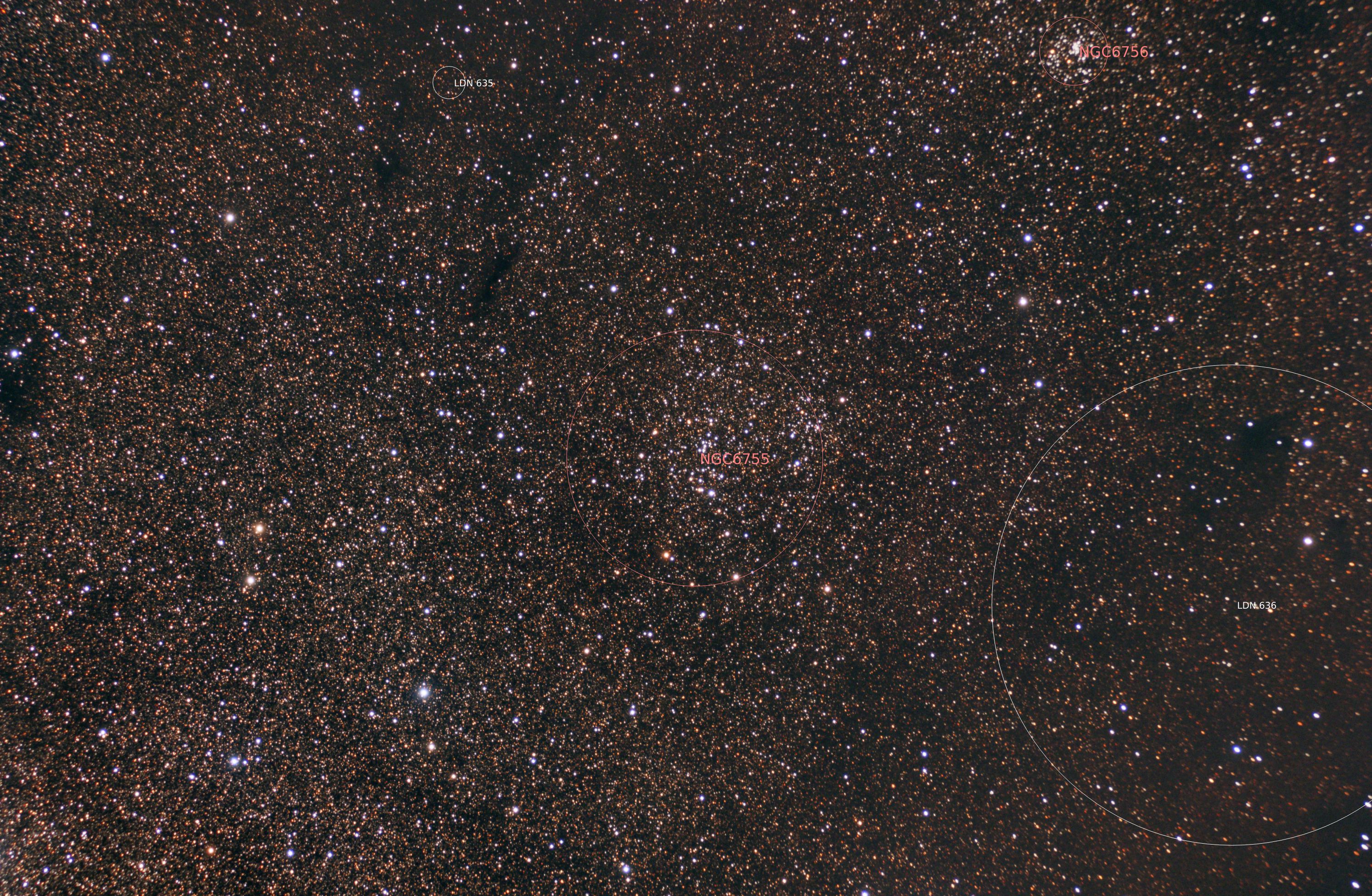

To the upper right is a unrelated small open cluster NGC 6756. NGC 6756 estimated distance is 6,363 light years.Image of NGC 6756 follows.
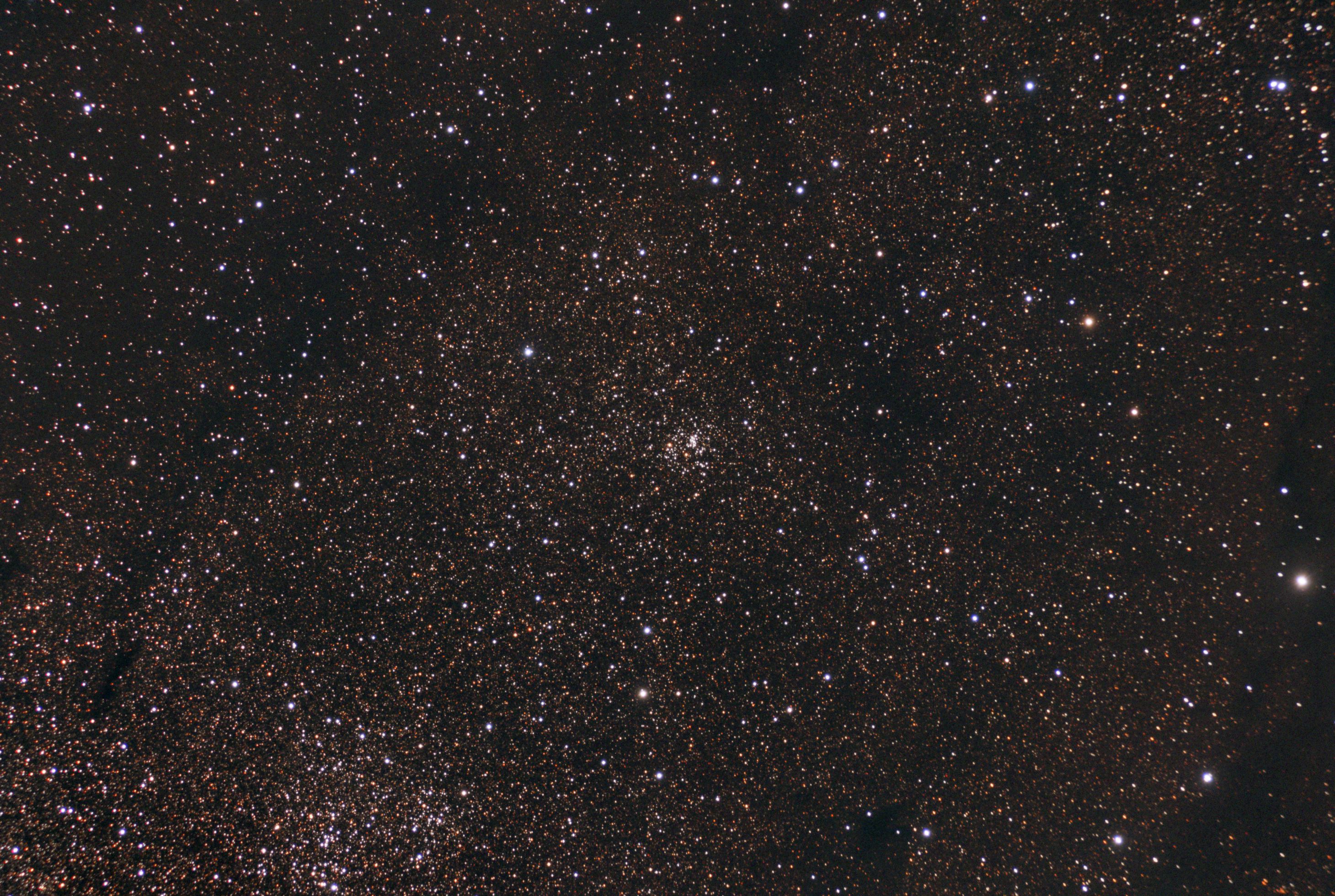

- Details
- Category: Open Clusters
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

NGC 6822 Barnard's Galaxy (2024)
- Constellation: Sagittarius
- Right Ascension: 19h 44m 56.6s
- Declination: −14° 47′ 21″
- Distance: 1.63 million ly
- Galaxy Type: IB(s)m
NGC 6822 is smaller barred irregular galaxy. It's the closest of the Local Group of galaxies that is not a satellite of the Milky Way Galaxy.
- Details
- Category: Galaxies
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

NGC 6384 Galaxy (2024)
- Constellation: Ophiuchus
- Right Ascension: 17h 32m 24.302s
- Declination: +07° 03′ 36.97″
- Distance: 77 million ly
- Galaxy Type: SAB(r)bc
NGC 6384 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Classified as a type SAB(r)bc galaxy with loosely wound spiral arms, and a central bar.
- Details
- Category: Galaxies
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

Wolf 359 (2024)
- Constellation: Leo
- Right Ascension: 10h 56m 28.92087s
- Declination: +07° 00′ 53.0033″
- Distance: 7.8 ly
- Apparent Magnitude: 13.5
- B-V Color Index: +2.034
Wolf 359 is a small dim red dwarf star located in the constellation of Leo. One of the stars studied by Max Wolf that exhibited high proper motion across the sky. Images taken in 2015, and 2024 showing its movement against the background stars.

- Details
- Category: Stars
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM

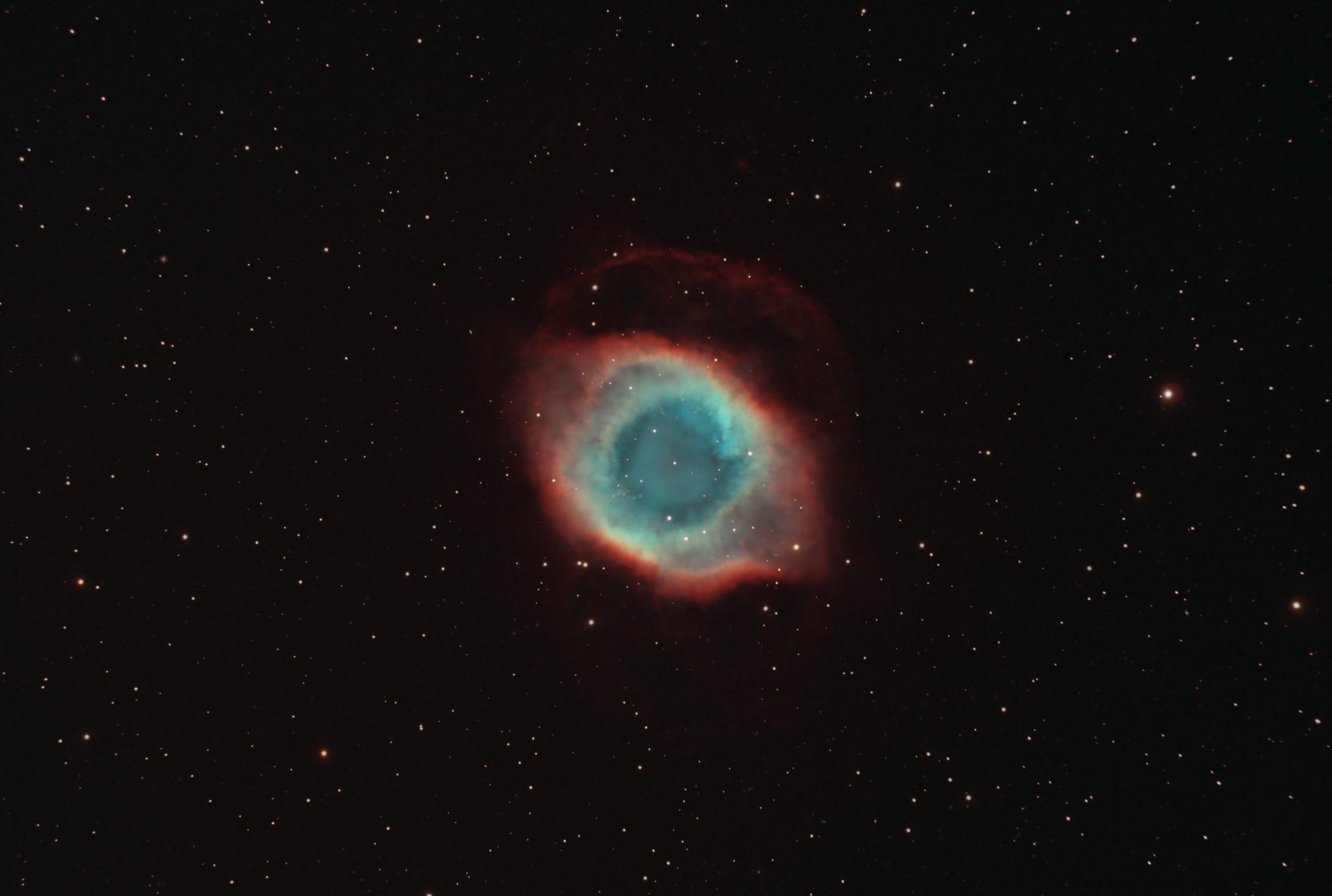
NGC 7293 Helix Nebula (2023)
- Constellation: Aquarius
- Right Ascension: 22h 29m 38.55s
- Declination: −20° 50′ 13.6″
- Distance: 650 ly
NGC 7293 aka Helix nebula is one of the closest of the planetary nebula which is formed from a lower mass star that sheds it's outer layers near the end of it's life before shrinking down to a white dwarf.
Following image taken using narrow band filters, Ha, OIII, and SII.
- Details
- Category: Nebulas
- Telescope: Explore Scientific 127 Refractor
- Camera: ZWO 2600 MM
Page 2 of 4









